Despite recent progress on inflation, cautious Federal Reserve policymakers now see only one rate cut this year.
Key Takeaways
- The Federal Reserve (Fed) left its target lending rate unchanged and now expects only one rate cut by year-end, down from its December forecast of three.
- Persistent inflation kept the Fed on hold, while easing inflation in Canada and Europe prompted the first rate cuts in developed markets.
- Amid slowing growth and inflation, we believe investors have time to pursue bond market opportunities before rates head lower.
The Fed’s Latest Decision
The Federal Reserve concluded its latest policy meeting on June 12 with no change to interest rates, marking the seventh consecutive meeting without a rate cut. Resilient economic growth and above-target inflation prevented the Fed from initiating the rate cuts hinted at in late 2023.
Despite some progress on inflation, including a slowdown in the May Consumer Price Index (CPI), Fed officials maintained the short-term interest rate target at a 23-year high of 5.25% to 5.5%. They now anticipate only one rate cut before year-end, a reduction from the three cuts forecasted in December.
Comparing Global Central Bank Actions
While the Fed holds steady, other central banks have started to cut rates. The Bank of Canada lowered its primary interest rate by a quarter point to 4.75% on June 5, and the European Central Bank followed with quarter-point cuts to key lending rates. The Bank of England may soon do the same. These moves come as inflation in Canada and Europe shows signs of easing, although it hasn’t yet reached target levels.
U.S. Economic Growth and Inflation Trends
Post-pandemic, the U.S. has seen stronger economic growth, lower unemployment rates, and more persistent inflation compared to its peers. For example, the U.S. economy grew at an annualized rate of 1.3% in the first quarter of 2024, significantly outpacing other developed markets.
Recent Economic Indicators
- U.S. GDP Growth: 2.5% in 2023
- U.S. Unemployment Rate: 4%
- U.S. Annualized Inflation Rate: 3.3%
U.S. Has Outpaced Its Peers
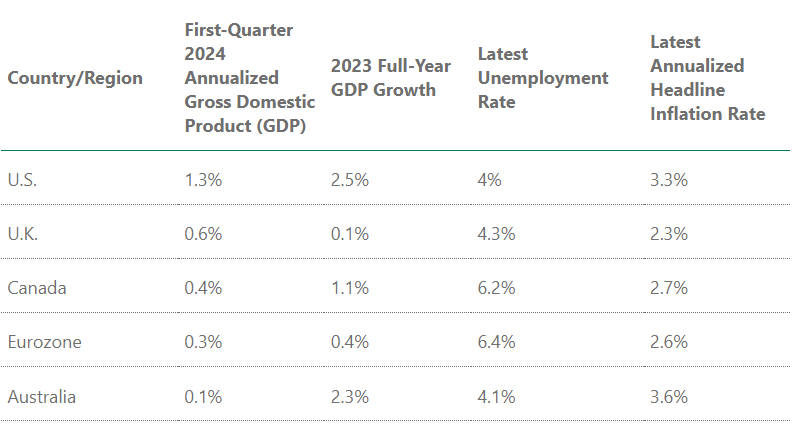
In contrast, other developed economies like the U.K., Canada, and the Eurozone have experienced weaker growth and higher unemployment rates, contributing to slowing inflation and prompting rate cuts.
The Impact on Investors
Given the Fed’s cautious approach, investors may find opportunities in the bond market before rates eventually decrease. The current environment suggests potential benefits from high-quality, short-duration bonds, which can capture attractive yields and reduce interest rate risk.
During economic downturns, high-quality bonds may provide stability to a diversified portfolio. When interest rates fall, bond prices typically rise, enhancing total return potential.
As we observe Annuity Awareness Month, it’s crucial to stay informed about how central bank policies affect investment strategies. While the Fed remains cautious, global peers are beginning to cut rates. This divergence offers unique opportunities for investors, particularly in the bond market. Stay tuned to economic trends and central bank actions to make informed decisions for your financial future.
